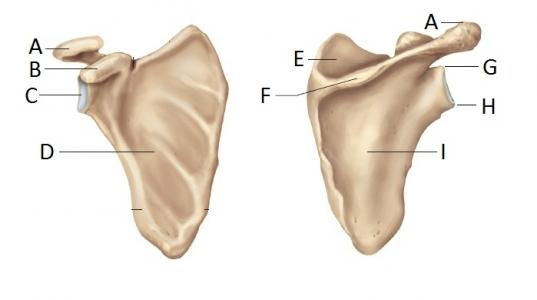
41 scapula bony landmarks quiz
Bony Landmarks: Types and Identification - Study.com Feb 25, 2022 · Many of the femur bony landmarks, can be found on this bone alone. Proximal epiphysis landmarks: At the proximal and medial end of the femur is the large round head which makes up the ball of the ... The Stomach - Structure - Neurovasculature - TeachMeAnatomy Sep 22, 2021 · Anatomical Structure Divisions of the Stomach. The stomach has four main anatomical divisions; the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus: Cardia – surrounds the superior opening of the stomach at the T11 level. Fundus – the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia. Body – the large central portion inferior to the fundus. ...
The Ribs - Rib Cage - Articulations - Fracture - TeachMeAnatomy Nov 04, 2021 · As part of the bony thorax, the ribs protect the internal thoracic organs. They also have a role in ventilation; moving during chest expansion to enable lung inflation. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the ribs – their bony landmarks, articulations and …
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/acromioclavicular-joint/H5h7l3PjocYJOJXPIxZOTw_Acromioclavikular_02.png)
Scapula bony landmarks quiz
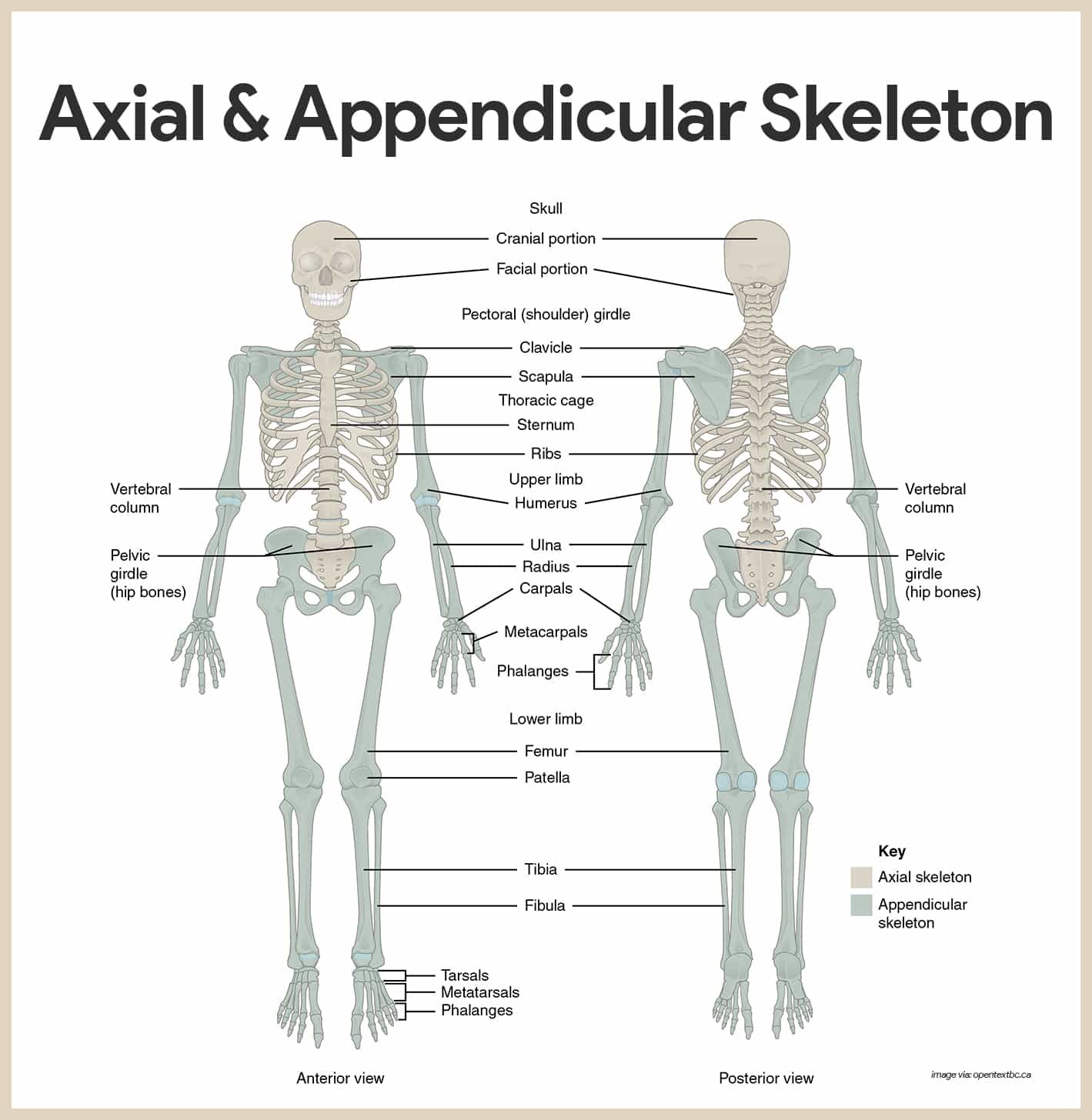
The Radius - Proximal - Distal - Shaft - TeachMeAnatomy May 10, 2020 · The radius is a long bone in the forearm. It lies laterally and parallel to ulna, the second of the forearm bones.The radius pivots around the ulna to produce movement at the proximal and distal radio-ulnar joints.. The radius articulates in four places: Elbow joint – Partly formed by an articulation between the head of the radius, and the capitulum of the humerus. Materials Objectives - Los Angeles Mission College The Language of Anatomy 3 Posterior Body Landmarks Note the following body surface regions (Figure 1.2b): Acromial: Point of the shoulder Brachial: Arm Calcaneal: Heel of the foot Cephalic: Head Dorsal: Back Femoral: Thigh Gluteal: Buttocks or rump Lumbar: Area of the back between the ribs and hips; the loin Manus: Hand Occipital: Posterior aspect of the head or base of the skull Chapter 7 Anatomy Flashcards | Quizlet Sinuses are solid, bony structures that function to strengthen the area around the orbit. Sinuses are non-ossified areas between the cranial bones that allow for growth. The paranasal sinuses are air-filled chambers lined with mucus-producing epithelium that open into the nasal cavities.
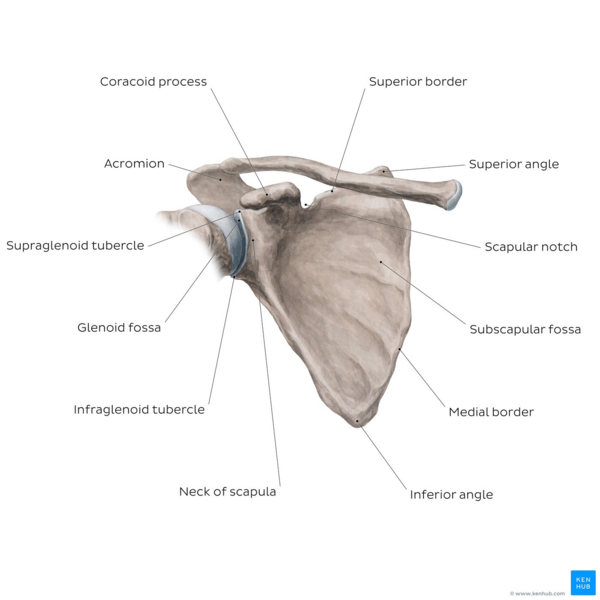
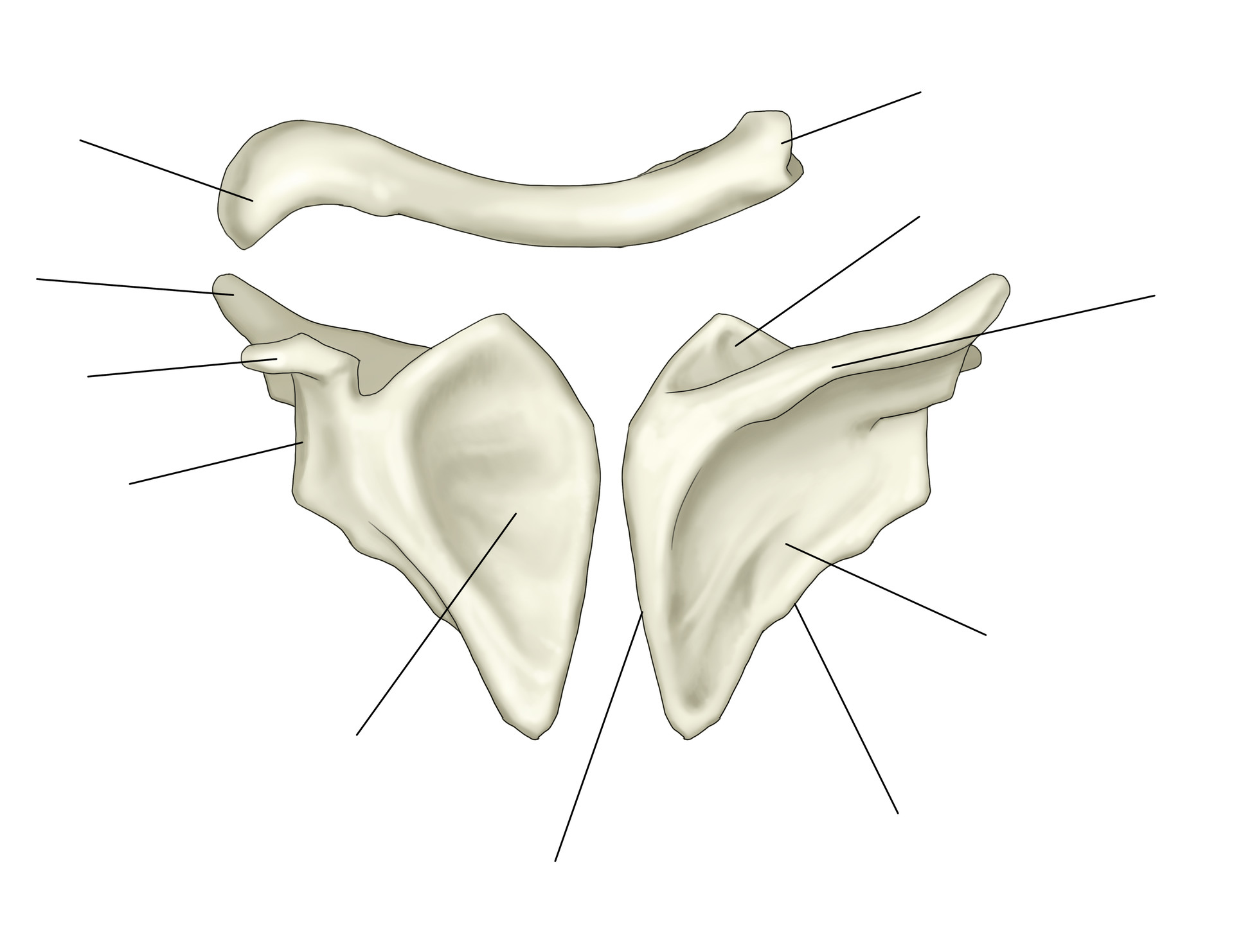
Scapula bony landmarks quiz. Sphenoid Bone - Location - Structure - Function - TeachMeAnatomy Sep 21, 2019 · The sphenoid bone is one of the eight bones that make up the cranium – the superior aspect of the skull that encloses and protects the brain.. Its name is derived from the Greek ‘sphenoeides’, to mean wedge-shaped. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the sphenoid bone – its location, structure, and clinical significance. Scapula: Anatomy and clinical notes | Kenhub Jul 08, 2022 · Like any triangle, the scapula consists of three borders: superior, lateral and medial. The superior border is the shortest and thinnest border of the three. The medial border is a thin border and runs parallel to the vertebral column and is therefore often called the vertebral border. The lateral border is often called the axillary border as it runs superolaterally towards the apex … Skeletal System • Anatomy & Function - GetBodySmart The clavicle or collarbone is located superior to the first rib and runs horizontally from the manubrium of the sternum to the acromion of the scapula. Sphenoid Bone The Sphenoid bone is a butterfly-shaped cranial bone that is located in the middle of the skull between the frontal and temporal bones. Bones of the Foot - Tarsals - Metatarsals - TeachMeAnatomy Apr 21, 2022 · These comprise the hindfoot, forming the bony framework around the proximal ankle and heel. Talus. The talus is the most superior of the tarsal bones. It transmits the weight of the entire body to the foot. It has three articulations: Superiorly – ankle joint – between the talus and the bones of the leg (the tibia and fibula).
Chapter 7 Anatomy Flashcards | Quizlet Sinuses are solid, bony structures that function to strengthen the area around the orbit. Sinuses are non-ossified areas between the cranial bones that allow for growth. The paranasal sinuses are air-filled chambers lined with mucus-producing epithelium that open into the nasal cavities. Materials Objectives - Los Angeles Mission College The Language of Anatomy 3 Posterior Body Landmarks Note the following body surface regions (Figure 1.2b): Acromial: Point of the shoulder Brachial: Arm Calcaneal: Heel of the foot Cephalic: Head Dorsal: Back Femoral: Thigh Gluteal: Buttocks or rump Lumbar: Area of the back between the ribs and hips; the loin Manus: Hand Occipital: Posterior aspect of the head or base of the skull The Radius - Proximal - Distal - Shaft - TeachMeAnatomy May 10, 2020 · The radius is a long bone in the forearm. It lies laterally and parallel to ulna, the second of the forearm bones.The radius pivots around the ulna to produce movement at the proximal and distal radio-ulnar joints.. The radius articulates in four places: Elbow joint – Partly formed by an articulation between the head of the radius, and the capitulum of the humerus.







![Scapula [skap′yələ] - one of the pair of large flat ...](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/24/5e/ee/245eee5066461cd3d4c114060364ccfb.jpg)

.jpg)













:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/superior-angle-of-scapula-1/9sovoFQAw0whi03K2ENsA_Superior_angle.png)




Komentar
Posting Komentar