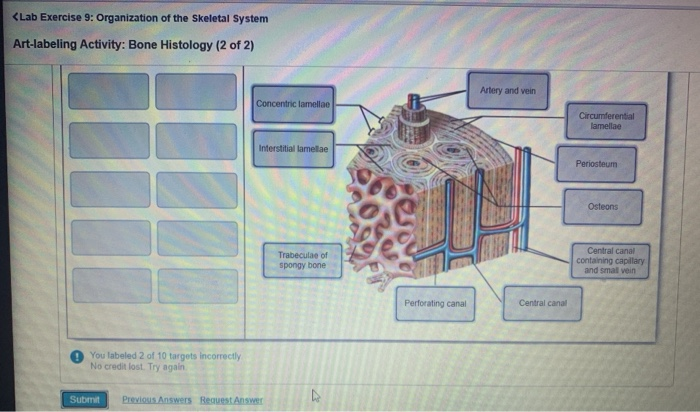
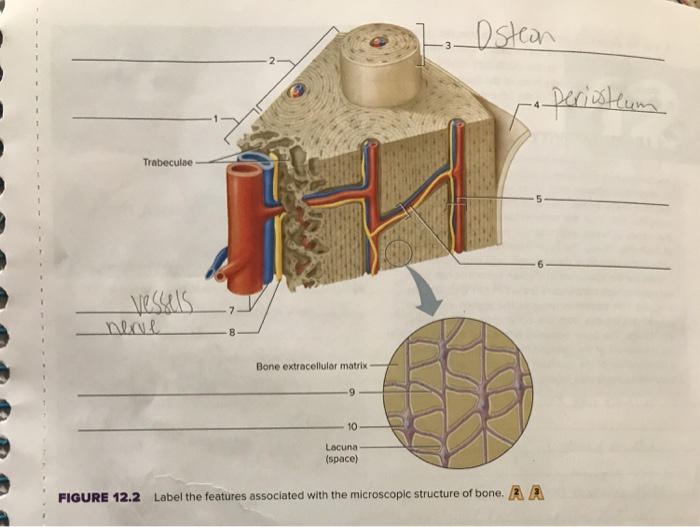
39 label the features associated with the microscopic structure of bone
The Osseous Tissue - Utrgv THE OSSEOUS TISSUE . FUNCTIONS • PROVIDE SUPPORT FOR OTHER TISSUES AND PROTECT UNDERLYING TISSUES • BONES ARE GOOD FOR STORAGE • HEMATOPOIESIS ( form blood cells ) TYPES OF BONE TISSUE. BY THE BONE STRUCTURE WE HAVE: SPONGY BONE - Lightweight, but able to withstand stress.; COMPACT BONE - Very dense and strong, found on the outside of all bones as a protective layer compact bone | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts compact bone, also called cortical bone, dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts, leaving only tiny spaces (lacunae) that contain the osteocytes, or bone cells. Compact bone makes up 80 percent of the human skeleton; the remainder is cancellous bone, which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces and is found in the ...
PDF Bones and Bone Structure - Palm Beach State College Section 1: Introduction to the Structure and Growth of Bones Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the two main divisions of the skeleton, and list the major functions of the skeletal system. 6.2 Classify bones according to their shapes, identify the major types of bone markings, and explain the functional significance of bone markings
Label the features associated with the microscopic structure of bone
Bone marrow: Histology, types and features | Kenhub Although it can be considered a "light-weight" system, the bone marrow does a lot of heavy lifting, as it is responsible for producing platelets, lymphocytes, erythrocytes, granulocytes, and monocytes. Marrow has two principal functions; one is to produce blood cells and the other is to store fat. microscopic bone labeling Flashcards | Quizlet circular channel running longitudinally in the center of an osteon of mature compact bone. Contains blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves. Small hollow space within bone matrix wherein resides an osteocyte. Located between concentric lamellae. Small channel connecting two lacuna in compact bone. Contains the cellular process of an osteocyte. Solved Trabeculae Bone extracellular matrix Lacuna (space) A | Chegg.com Trabeculae Bone extracellular matrix Lacuna (space) A FIGURE 12.2 Label the features associated with the microscopic structure of bone. Osteon Lamella Bone extracellular matrix Central canal Lacuna (occupled by osteocyte in living bone) Canaliculi (Victor B. Eichler, Ph.D f und compact bone tissue (200x). APIR
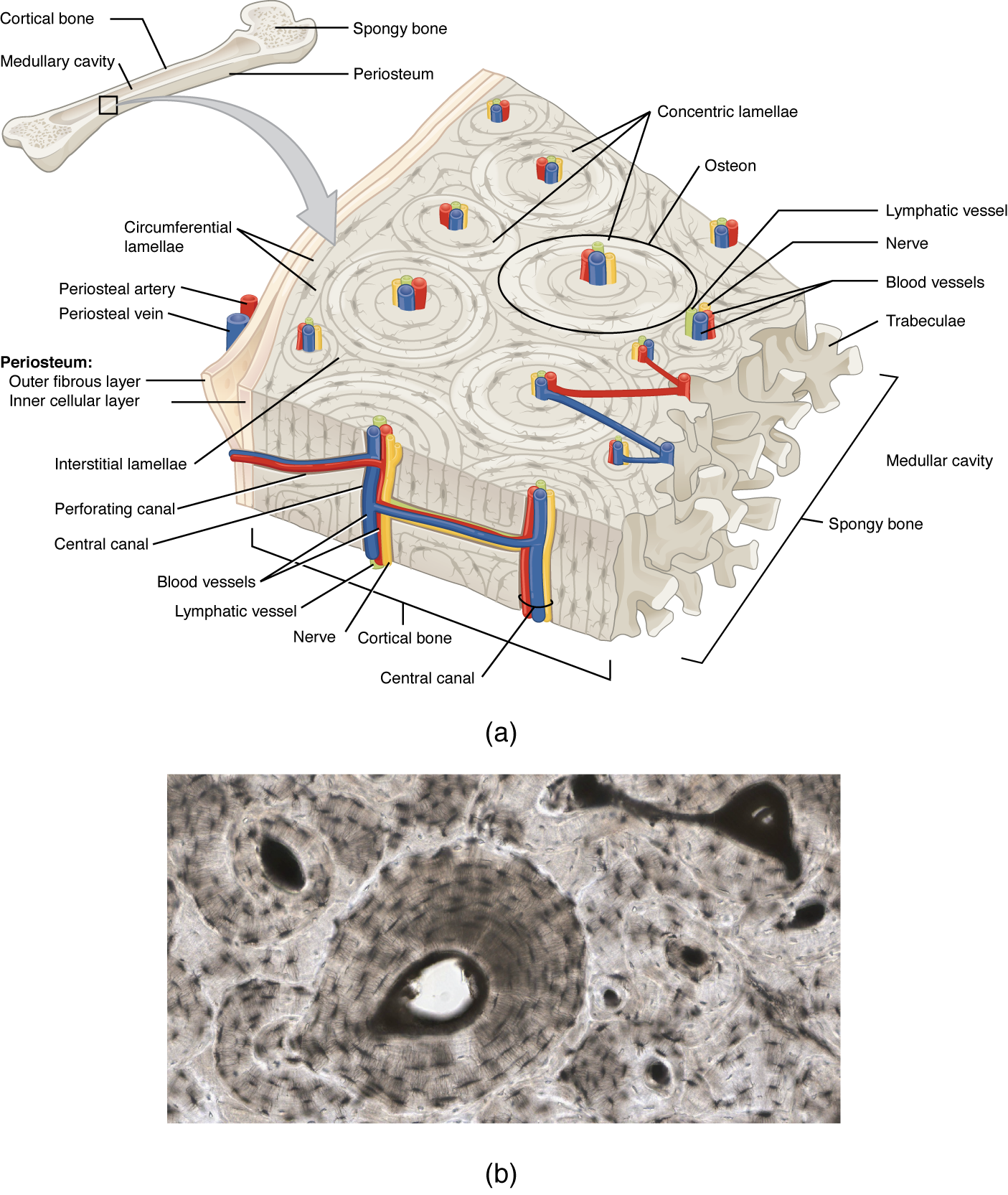
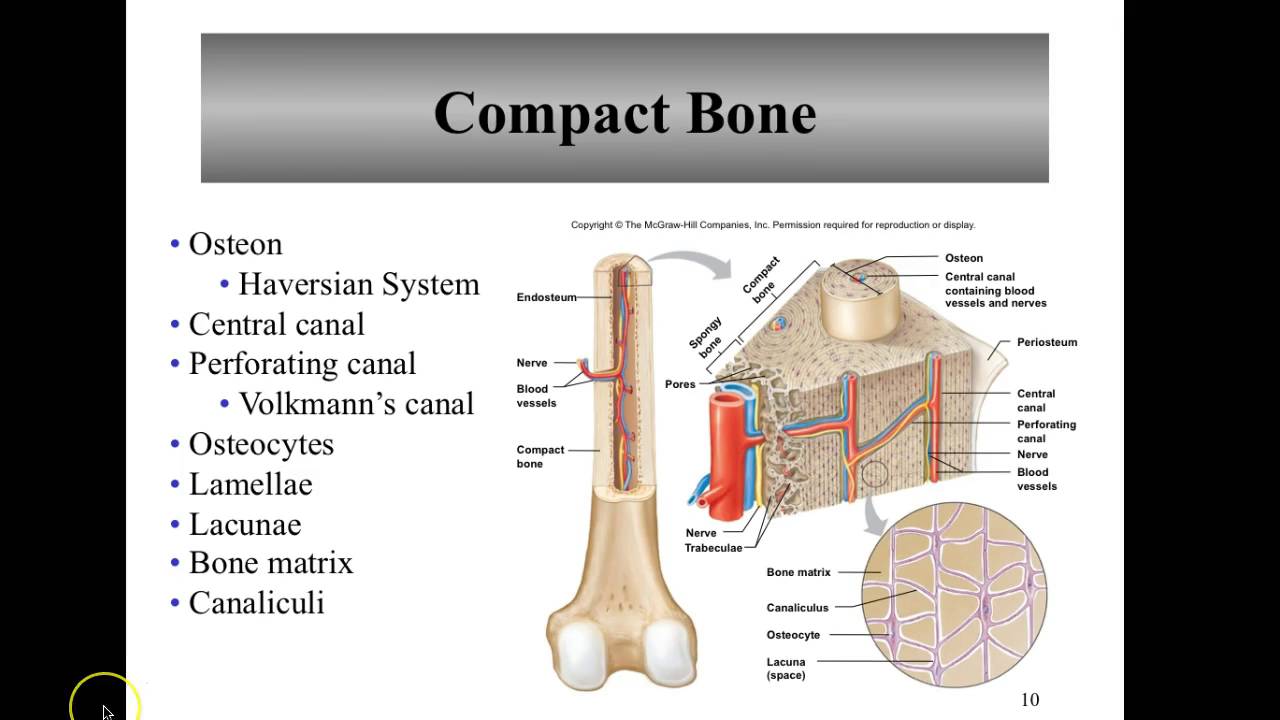
Label the features associated with the microscopic structure of bone. Skeletal Muscle: What Is It, Function, Location & Anatomy The majority of the muscles in your body are skeletal muscles. They make up between 30 to 40% of your total body mass. Tendons (tough bands of connective tissue) attach skeletal muscle tissue to bones throughout your body. Your shoulder muscles, hamstring muscles and abdominal muscles are all examples of skeletal muscles. Histology - Yale University Microscopic Bone Structure Compact bone is organized as parallel columns, known as Haversian systems, which run lengthwise down the axis of long bones. These columns are composed of lamellae, concentric rings of bone, surrounding a central channel, or Haversian canal, that contains the nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic system of the bone. Bone Structure - Anatomy & Physiology - University of Hawaiʻi The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal, or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. Structure of Skeletal Muscle | SEER Training Typically a muscle spans a joint and is attached to bones by tendons at both ends. One of the bones remains relatively fixed or stable while the other end moves as a result of muscle contraction. Skeletal muscles have an abundant supply of blood vessels and nerves. This is directly related to the primary function of skeletal muscle, contraction.
Spongy Bone (Cancellous Bone) - Definition & Function | Biology Bone marrow, also called myeloid tissue, is formed when the trabecular matrix crowds blood vessels together and they condense. While compact bone is denser and has fewer open spaces, spongy bone is ideal for making and storing bone marrow within the lattice-like trabeculae network. Page: The Journal of Pediatrics Dec 04, 2019 · A 13-year-old presented with extreme thirst and increased urine production. MR imaging showed a thickened pituitary stalk. After biopsy, the patient was diagnosed with Langerhans cell histiocytosis. After two years, a follow-up MRI showed lesions on the left temporal bone, suggesting LCH relapse. See the full report here. Bones: Types, structure, and function - Medical News Today Studies show that, in addition to structure and movement, bones support energy metabolism, the production of blood cells, the immune system, and brain function. Mechanics Bones provide a frame to... Compact Bone Structure | Biology Dictionary Compact Bone Structure. Compact bone, also called cortical bone, is the hard, stiff, smooth, thin, white bone tissue that surrounds all bones in the human body. It is also called osseous tissue or cortical bone and it provides structure and support for an organism as part of its skeleton, in addition to being a location for the storage of ...
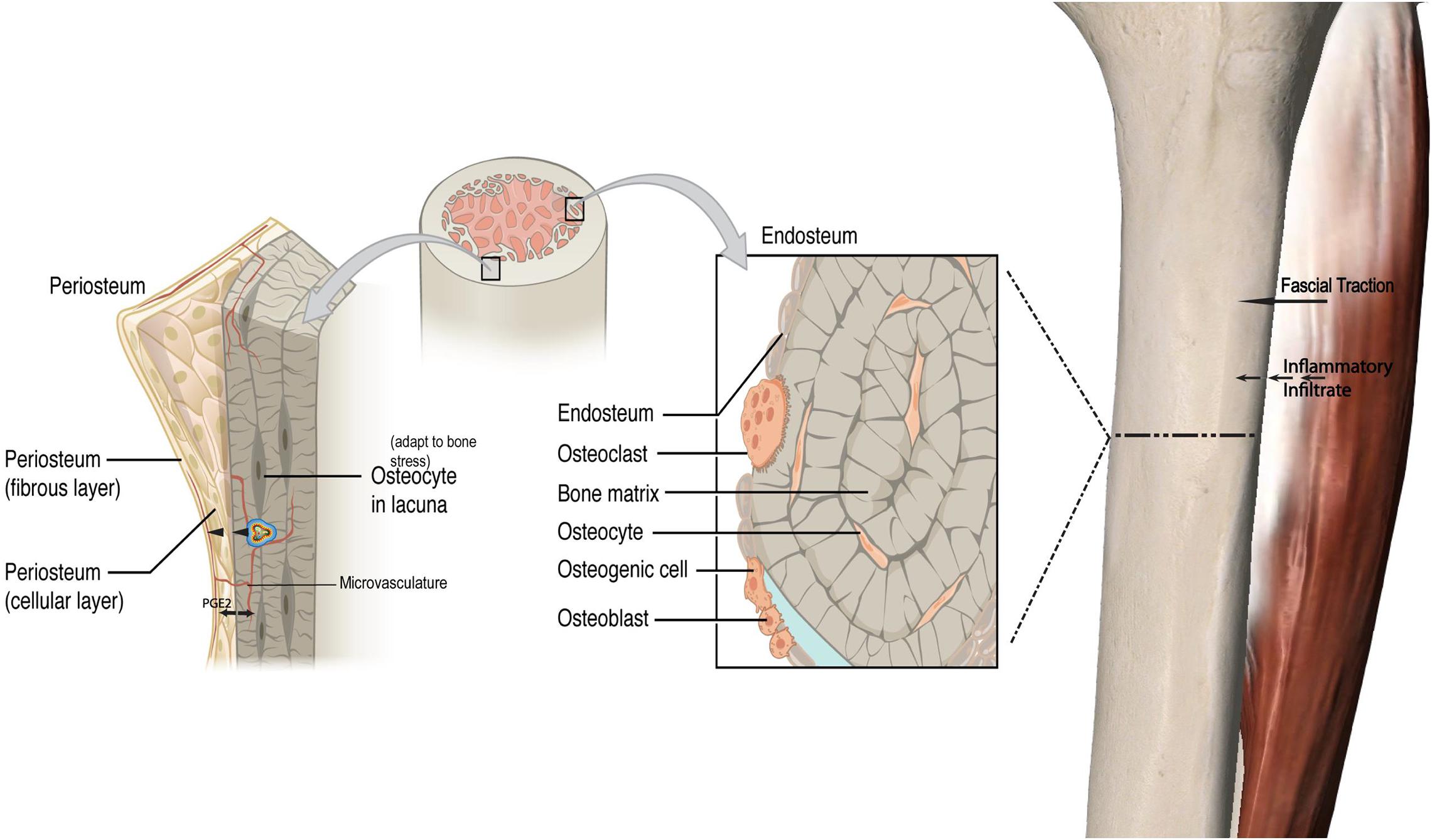
PDF Bone Structure Description Lab - MR. BURKE Label the following structures in the figure below 1) External acoustic meatus 2) Foramen magnum 3) Mastoid process 4) Occipital bone 5) Occipital condyle 6) Palatine process of maxilla 7) Sphenoid bone 8) Temporal bone 9) Vomer bone 10) Zygomatic bone Types of Bone Cells | Osteoclasts, Osteoblasts, & Osteocytes - Bio Explorer Types of Bone Cells: The bones are a core founding component of a living body that holds the structure of muscles and organs.The bones of the skeletal system are composed of two types of tissues, i.e., compact and spongy bone tissue.. The Compact bone tissue covers the outer part of the bone structure and provides toughness and strength to the structure of bone. 6.3 Bone Structure - Anatomy and Physiology 2e | OpenStax The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal, or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence ... 1. Introduction. Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [1, 2].Bone exerts important functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection of soft tissues, calcium and phosphate storage, and harboring of bone marrow [3, 4].Despite its inert appearance, bone is a highly dynamic organ that ...
› departments › computer-visionMax-Planck-Institut für Informatik: Publications On the label-level, we employ a bilateral mixed sampling strategy to augment the target domain, and a relabelling method to unify and align the label spaces. We address the image-level domain gap by proposing an uncertainty-rectified contrastive learning method, leading to more domain-invariant and class discriminative features.
› pmc › articlesVascular complications of diabetes: mechanisms of injury and ... Jan 01, 2013 · Some of the main features are accumulation of lipid-laden macrophages in the atherosclerotic plaque and subsequent macrophage apoptosis (left); podocyte apoptosis, thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, and breakdown of the filtration barrier in the renal glomeruli (middle); and pericyte and endothelial cell apoptosis, vascular leakage ...
Page: Fertility and Sterility Sep 07, 2020 · Fertility and Sterility® is an international journal for obstetricians, gynecologists, reproductive endocrinologists, urologists, basic scientists and others who treat and investigate problems of infertility and human reproductive disorders.
Skeletal System - Labeled Diagrams of the Human Skeleton - Innerbody The skeletal system in an adult body is made up of 206 individual bones. These bones are arranged into two major divisions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton runs along the body's midline axis and is made up of 80 bones in the following regions: Skull Hyoid Auditory ossicles Ribs Sternum Vertebral column
Bone Structure | Anatomy and Physiology I | | Course Hero The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal, or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
compact bone anatomy lacuna 33 Label The Features Associated With The Microscopic Structure Of Bone dandelionsandthings.blogspot.com microscopic extracellular csls trabeculae solved matrix Spongy Bone Tissue - Stock Image P105/0065 - Science Photo Library bone spongy tissue sciencephoto april enlarge biology Osseous Tissue (Compact Bone) - Human Body Help
Structure Of Bone - Human Anatomy - GUWS Medical 1. Reexamine the microscopic structure of bone tissue by observing a prepared microscope slide of ground compact bone. Use the figures of bone tissue in a textbook to locate the following features: osteon (Haversian system) osteonic canal (Haversian canal) lamella lacuna (small chamber for an osteocyte) canaliculus Critical Thinking Application
Solved us Trabeculae CSLS ea 8 Bone extracellular matrix 10 ... - Chegg Question: us Trabeculae CSLS ea 8 Bone extracellular matrix 10- Lacuna (space) FIGURE 12.2 Label the features associated withthe microscopic structure of bone. A A This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (2 ratings) 6. Perforating canal 5. Arte … View the full answer
Structure of Bone Tissue | SEER Training - National Cancer Institute Spongy (cancellous) bone is lighter and less dense than compact bone. Spongy bone consists of plates ( trabeculae) and bars of bone adjacent to small, irregular cavities that contain red bone marrow. The canaliculi connect to the adjacent cavities, instead of a central haversian canal, to receive their blood supply.
10.2 Skeletal Muscle - Anatomy and Physiology 2e | OpenStax Each skeletal muscle is an organ that consists of various integrated tissues. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called "mysia") that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also ...
Urological Association CUSTOMER SERVICE: Change of address (except Japan): 14700 Citicorp Drive, Bldg. 3, Hagerstown, MD 21742; phone 800-638-3030; fax 301-223-2400.
› pmc › articlesHUMAN HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT FOR ALUMINIUM, ALUMINIUM OXIDE ... Slightly > 90% of plasma aluminium is associated with transferrin (Tf), ~ 7 to 8% with citrate, and < 1% with phosphate and hydroxide. Normal plasma aluminium concentration is believed to be 1 to 2 μg/L. Normal tissue aluminium concentrations are greater in lung (due to entrapment of particles from the environment) than bone than soft tissues.
Histology, Bone - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Cortical Bone: consists of about 80% of the total bone in the body and is much stronger than trabecular bone. It is very resistant to bending, torsion, and compression and is much more dense with a minimal role in metabolism. It is seen mostly in the shaft of long bones like the femur and the tibia as well as in the outer shell of trabecular bone.
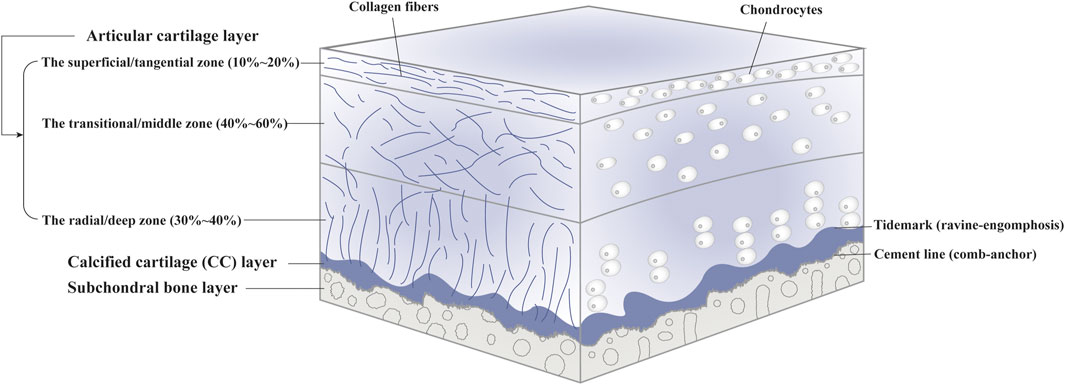
Bone Histology - Embryology - UNSW Sites This practical class will describe the development and structure of bone and finish with a study of abnormalities associated with bone. The image shown to the left shows a histological section through the developing lower limb at the level of a developing joint (knee), surrounding the developing bone are skeletal muscles and connective tissue ...
Quiz: Bone Structure - CliffsNotes Surface Features of Bones; Quiz: Surface Features of Bones; The Skeletal System. Quiz: Skull: Cranium and Facial Bones; ... Previous Bone Structure. Next Bone Development. Quiz: What is Anatomy and Physiology? Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds ... Removing #book# from your Reading List will also remove any bookmarked pages associated with this ...
Lab Report 12 Bone Structure and Classification - Quizlet Figure 12.2 features associated with the microscopic structure of bone. 1. Spongy Bone 2. Compact Bone 3. Osteon 4. Periosteum 5. Central Canal 6. Perforating Canal 7. Blood Vessels 8. Nerve 9. Canaliculus 10. Osteocyte A bone that is platelike is classified as a (n) ________ bone. Flat The bones of the wrist are examples of _______ bones. Short
Structure and Function of the Haversian System Explained ... - Bodytomy The terms 'Haversian system' or 'osteon' refer to the basic cylindrical-shaped structural unit of a compact bone, which in turn forms a substantial part of the structure of the long bones of the human body. The osteons are closely packed, with osteocytes lined up in concentric rings. This imparts a hard and dense texture to the compact ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Prostate_cancerProstate cancer - Wikipedia Early prostate cancer usually has no clear symptoms. When they do appear, they are often similar to those of benign prostatic hyperplasia.These include frequent urination, nocturia (increased urination at night), difficulty starting and maintaining a steady stream of urine, hematuria (blood in the urine), dysuria (painful urination) as well as fatigue due to anemia, and bone pain.
Solved Trabeculae Bone extracellular matrix Lacuna (space) A | Chegg.com Trabeculae Bone extracellular matrix Lacuna (space) A FIGURE 12.2 Label the features associated with the microscopic structure of bone. Osteon Lamella Bone extracellular matrix Central canal Lacuna (occupled by osteocyte in living bone) Canaliculi (Victor B. Eichler, Ph.D f und compact bone tissue (200x). APIR
microscopic bone labeling Flashcards | Quizlet circular channel running longitudinally in the center of an osteon of mature compact bone. Contains blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves. Small hollow space within bone matrix wherein resides an osteocyte. Located between concentric lamellae. Small channel connecting two lacuna in compact bone. Contains the cellular process of an osteocyte.
Bone marrow: Histology, types and features | Kenhub Although it can be considered a "light-weight" system, the bone marrow does a lot of heavy lifting, as it is responsible for producing platelets, lymphocytes, erythrocytes, granulocytes, and monocytes. Marrow has two principal functions; one is to produce blood cells and the other is to store fat.






















Komentar
Posting Komentar